in Operatordel StatementAre there any questions before I begin?
I have posted homework 11 here.
This is the last homework assignment.
It is due this coming Sunday at 11:59 PM.
for loop
>>> for team in teams: ... print(team) ... Red Sox Orioles Blue Jays Rays Yankees
>>> for index in range(len(teams)): ... print(teams[index]) ... Red Sox Orioles Blue Jays Rays Yankees
for loop ...>>> name = "Glenn" + " " + "Hoffman" >>> name 'Glenn Hoffman'
>>> l1 = [1,2,3] >>> l2 = [4,5,6] >>> l1 + l2 [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6]
>>> l1 / l2
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "<stdin>", line 1, in <module>
TypeError: unsupported operand type(s) for /: 'list' and 'list'
>>> zeros = [0] * 5 >>> zeros [0, 0, 0, 0, 0] >>> numbers = [1, 2, 3] * 3 >>> numbers [1, 2, 3, 1, 2, 3, 1, 2, 3]
>>> "Go " * 3 'Go Go Go '
LIST_VARIABLE[INDEX]
even_numbers = [2,4,6,8]

>>> even_numbers[0] 2 >>> even_numbers[1] 4 >>> even_numbers[2] 6
numbers = [1, 4, 6, 8]
>>> numbers[0] = 2 >>> numbers [2, 4, 6, 8]
for looprange ...len built-in
function
for loop
>>> for i in range(len(numbers)): ... numbers[i] += 1 ... >>> numbers [3, 5, 7, 9]
range I mentioned
something that seemed strange
range was called with a single number ...range works this way ...
LIST_VARIABLE[FIRST_INDEX:ONE_MORE_THAN_LAST_INDEX]
>>> days = ["Sunday", "Monday", "Tuesday", "Wednesday", "Thursday", "Friday", "Saturday"]
>>> weekdays = days[1:6] >>> weekdays ['Monday', 'Tuesday', 'Wednesday', 'Thursday', 'Friday']
>>> days ['Sunday', 'Monday', 'Tuesday', 'Wednesday', 'Thursday', 'Friday', 'Saturday'] >>> days[:4] ['Sunday', 'Monday', 'Tuesday', 'Wednesday'] >>> digits = [0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9] >>> digits[:5] 0, 1, 2, 3, 4]
>>> days[4:] ['Thursday', 'Friday', 'Saturday'] >>> digits[5:] [5, 6, 7, 8, 9]
>>> days[:] ['Sunday', 'Monday', 'Tuesday', 'Wednesday', 'Thursday', 'Friday', 'Saturday'] >>> digits[:] [0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9]
>>> daynames = days[:] >>> daynames ['Sunday', 'Monday', 'Tuesday', 'Wednesday', 'Thursday', 'Friday', 'Saturday']
range function
LIST_VARIABLE[FIRST_INDEX:ONE_MORE_THAN_LAST_INDEX:STEP_VALUE]
>>> digits = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 0] >>> digits[0:9:2] [0, 2, 4, 6, 8]
digits[0::2] [0, 2, 4, 6, 8]
digits[::2] [0, 2, 4, 6, 8]
in Operatorin is an operator that works on objects
that are a collection of values
VALUE in LIST
in operator returns True if the
LIST contains VALUE
False
>>> digits [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 0] >>> 1 in digits True >>> 11 in digits False
| Method | Description |
|---|---|
| append(item) | Adds item to the end of the list |
| pop(index) | Removes the element at a given index from the list and returns the
value. If called with no argument, it returns the last element and deletes it from the list. |
| sort() | Sorts the items in the list so they appear in ascending order (from the lowest value to the highest value) |
| reverse() | Reverses the order of the items in the list |
>>> teams = [] >>> teams []
>>> teams.append("Red Sox")
>>> teams
['Red Sox']
>>> teams.append("Orioles")
>>> teams.append("Blue Jays")
>>> teams.append("Rays")
>>> teams.append("Yankees")
>>> teams ['Red Sox', 'Orioles', 'Blue Jays', 'Rays', 'Yankees']
>>> numbs = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5] >>> n = numbs.pop(0) >>> n 1 >>> numbs [2, 3, 4, 5]
>>> n = numbs.pop() >>> n 5 >>> numbs [2, 3, 4]
>>> l2 = [9, 1, 0, 2, 8, 6, 7, 4, 5, 3] >>> l2 [9, 1, 0, 2, 8, 6, 7, 4, 5, 3] >>>l2.sort() >>> l2 [0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9]
>>> l3 = [5, 4, 3, 2, 1] >>> l3.reverse() >>> l3 [1, 2, 3, 4, 5] >>> l3.reverse() >>> l3 [5, 4, 3, 2, 1]
>>> l4 = [2, 5, 9, 1, 8, 6, 3, 7, 4] >>> l4.sort() >>> l4 [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9]
>>> l4.reverse() >>> l4 [9, 8, 7, 6, 5, 4, 3, 2, 1]
del Statementdel statement
del LIST_VARIABLE[INDEX]
del comes the list variable ...>>> l5 = [0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5] >>> del l5[2] >>> l5 [0, 1, 3, 4, 5]
min and max ...
min returns the smallest value in a list
>>> l6 [1, 4, 5, 6] >>> min(l6) 1
max returns the largest
max(l6) 6
file = open("numbs.txt", "r")
total = 0
count = 0
for line in file:
number = int(line)
total += number
count += 1
average = round(total/count)
file.close()
file = open("numbs.txt", "r")
above_average = 0
for line in file:
number = int(line)
if number > average:
above_average += 1
create an empty list
for each line in the file:
append the line to the empty list
file = open("numbs.txt", "r")
numbers = []
for line in file:
numbers.append(int(line))
total = 0
for num in numbers:
total += num
average = round(total/len(numbers))
above_average = 0
for num in numbers:
if num > average:
above_average += 1
print(above_average)
len on the list variablefor loops
for loop
file = open("numbs.txt", "r")
total = 0
numbers = []
for line in file:
num = int(line)
numbers.append(num)
total += num
average = round(total/len(numbers))
above_average = 0
for num in numbers:
if num > average:
above_average += 1
print(above_average)
len on the list object
set a variable to a very low value
for each value in the file:
if the value is greater than the variable:
set the variable to this new value
max to get the largest valuemin to get the smallestfor loop to create a list ...>>> n1 = 5
>>> n2 = n1 >>> n2 5
>>> n1 = 6 >>> n1 6 >>> n2 5
>>> l1 = [1,2,3,4,5,6,7] >>> l1 [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7]
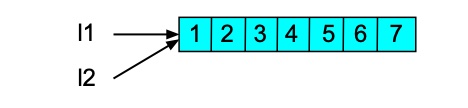
>>> l2 = l1 >>> l2 [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7]
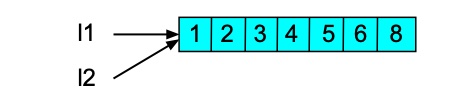
>>> l1[6] = 8 >>> l1 [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 8] >>> l2 [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 8]
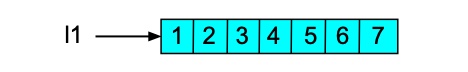
>>> l2 = l1
>>> l1[6] = 8
>>> l1
[1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7]
>>> l2 = [] + l1
>>> l2
[1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7]
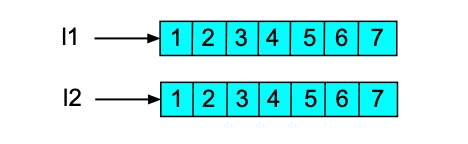
>>> l1[6] = 8 >>> l1 [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 8] >>> l2 [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7]
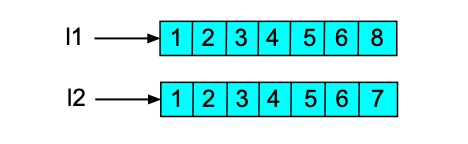
>>> l1 = [1,2,3,4,5,6,7]
>>> l2 = l1[0:len(l1)]
>>> l1[6] = 9
>>> l1
[1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 9]
>>> l2
[1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7]
>>> l1 = [1,2,3,4,5,6,7]
>>> l2 = l1[:]
>>> l1.append(8) = 10
>>> l1
[1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8]
>>> l2
[1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7]
use the filename to create a file object
create an empty list
for each line in the file:
convert the line into a number
add the number to the empty list
return a variable pointing to the list
#! /usr/bin/python3
# reads a text file containing integers
# and prints it
# reads a text file of integers
# and stores them in a list which is returned
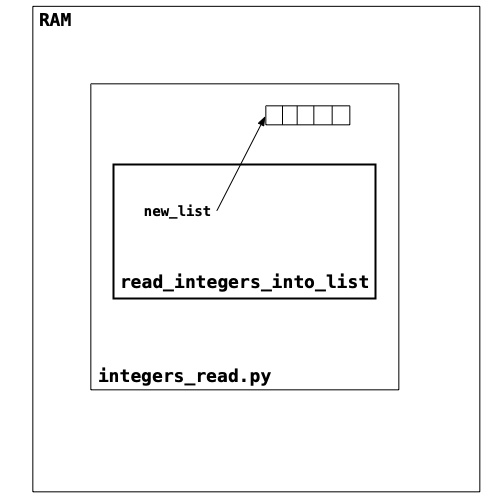
def read_integers_into_list(filename):
file = open(filename, "r")
new_list = []
for line in file:
number = int(line)
new_list.append(number)
file.close()
return new_list
number_list = read_integers_into_list("temperatures.txt")
print("List:", number_list)
$ ./integers_read.py List: [76, 67, 74, 76, 84, 69, 67, 76, 66, 71]
set total to zero
loop through the list using the list variable:
add each number to total
return the total divided by the length of the list
def average_list(list):
total = 0
for number in list:
total += number
return total/len(list)
def entries_above(list, value):
number_above = 0
for number in list:
if number > value:
number_above += 1
return number_above
#! /usr/bin/python3
# this script reads in daily temperatures from a file and
# calculates the numbers of days with above average temperatures
# reads integers into a list
def read_integers_into_list(filename):
file = open(filename, "r")
new_list = []
for line in file:
number = int(line)
new_list.append(number)
file.close()
return new_list
# returns the average of list of numbers
def average_list(list):
total = 0
for number in list:
total += number
return total/len(list)
# returns the number of entries in a list
# above a certain value
def entries_above(list, value):
number_above = 0
for number in list:
if number > value:
number_above += 1
return number_above
temps = read_integers_into_list("temperatures.txt")
print("Temperature list:", temps)
average = average_list(temps)
print("Average:", average)
print("Days above average:", entries_above(temps, average))
$ ./above_average_2.py Temperature list: [76, 67, 74, 76, 84, 69, 67, 76, 66, 71] Average: 72.6 Days above average: 5
>>> def double_list(list): ... for index in range(len(list)): ... list[index] = 2 * list[index] ... >>> numbers = [1,2,3,4,5] >>> double_list(numbers) >>> numbers [2, 4, 6, 8, 10]